- cross-posted to:
- space@lemmit.online
- cross-posted to:
- space@lemmit.online
Uh oh…
I would like to know more.
 Luckily we are in another location.
Luckily we are in another location.
Is it Space? I sure hope it is.
Probably Space Communist

If I catch you damn space kids throwing rocks at my planet again and I’ll call the galatic police!
Alien kid with a giant catapult: “it wasn’t me”
I see you there space Billy, I’ll tell your mom you’re playing with those Martian boys again!
It wasn’t me, inyalowda.

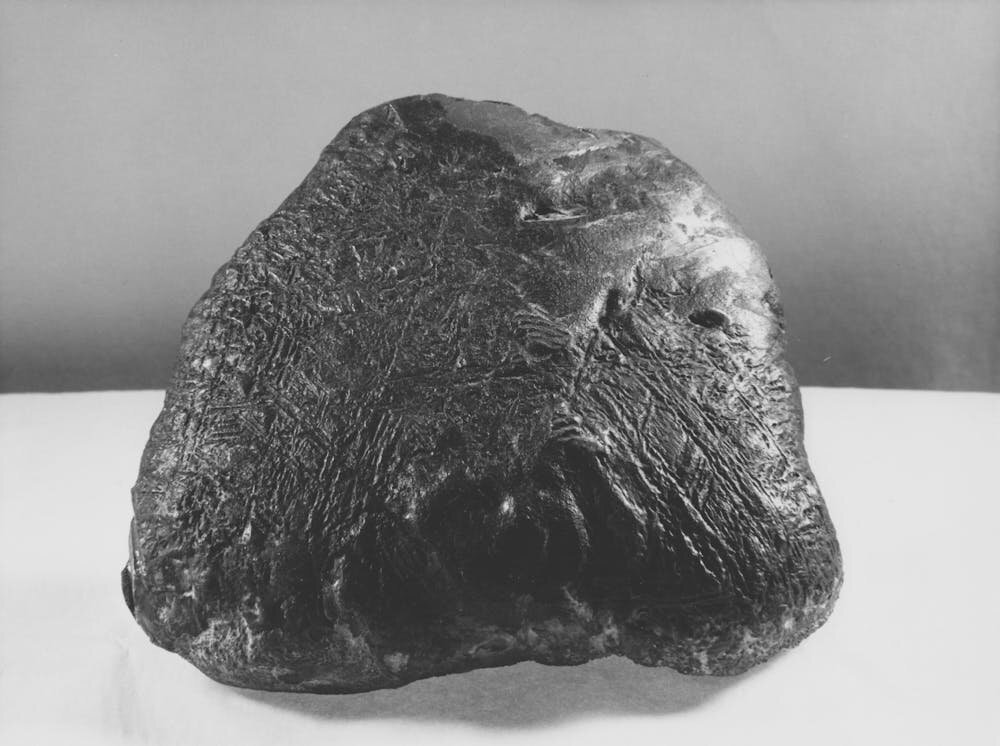
So to sum up the article, most meteorites (the ones that actually hit earth) are the result of just a few (perhaps three) large asteroid collisions some time in the past.
Most asteroids seem to be in relatively stable orbits which is basically necessary for them to still be orbiting. So it follows that it would take something altering that orbit for them to end up in an earth intercept course. Ejecta from a collision makes sense.
I guess the truly surprising part is that most of the samples we have are such good matches that we can conclude they belonged to the same individual asteroids.
Marco Inaros is just getting started.
That just a big ol’ frozen chunk of poopy.
‘You ate off that thing’
That’s a space peanut!
Is that source “space” or “the solar system”?
So they mostly come from the asteroid belt, which itself is likely a few large bodies that got ripped apart by Jupiter and each other… This isn’t surprising at all, just confirmation of what was assumed already.
The speculation that “most” of the ~17,000 meteorites that fall each year come from just a couple specific asteroids within the asteroid families seems like overweighted nonsense to me, though. They don’t really seem to have a way to verify that, just modeling of an event 470 million years ago, and composition. They just know that they likely come from a few asteroid families, which can contain thousands of individual asteroids (though it’s also entirely possible that portions of the asteroid family were ripped away and obliterated in a separate event), possibly with very similar or identical makeup, so to then assert they “may” or “very likely” (both terms used in the article) come from a singular asteroid within the asteroid family is giving this research way way more weight than it should have, imho.
Unless they are trying to say (it’s early and I just woke up, so that may be it) that the original large body that was broken up is the source, but that’s so intensely “no shit, Sherlock” as to be basically meaningless. After all, the entire belt is a result of those large body breakups, and the asteroid families responsible for the meteors are quite sizable (three of the named ones, Flora, Massalia, and Koronos, contain a combined ~27,000 bodies)











